FAQ
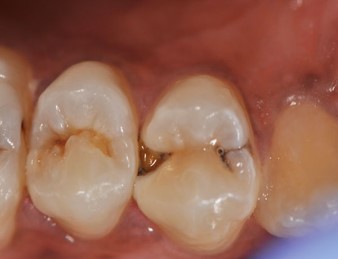
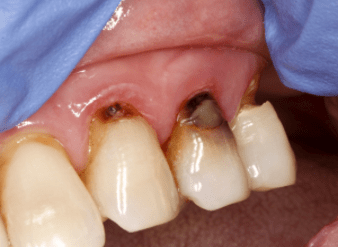
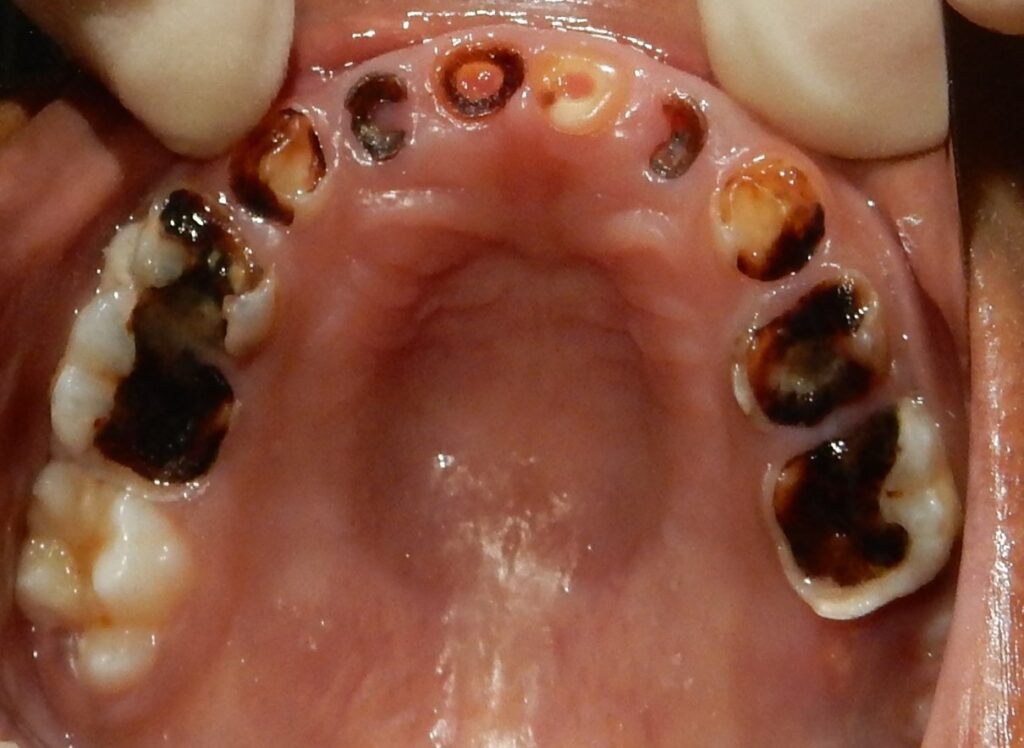
CARIES & CAVITIES
Tooth decay occurs as teeth are frequently exposed to foods containing carbohydrates (starches and sugars) like chocolates, sweets, ice creams, cakes, and even fruits, vegetables and juices. Oral cavity contains numerous bacteria and these bacteria forms plaque. The plaque interacts with deposits of food left on teeth from sugars and starch to produce acids. These acids in turn damage the tooth enamel over a period of time by demineralizing the structure of teeth, resulting in tooth decay and weakened teeth.
Prevention of Caries
Acids formed by plaque are usually countered by saliva in your mouth, which acts as a buffer. Dentists often recommend chewing sugarless gum to stimulate your flow of saliva. However, saliva alone is not sufficient to combat tooth decay. The best way to prevent caries is to maintain a healthy oral hygiene, which essentially translates to brushing and flossing regularly. Early damage by plaque can be countered by the use fluoride, which helps to re-mineralize the tooth structure. Fluoride is a regular ingredient of toothpastes to fight cavities and clean teeth. If you are at medium to high risk for cavities, your dentist may recommend special high concentration fluoride gels, mouth rinses, or dietary fluoride supplements.
Risk of caries
We all carry bacteria in our mouth, making us prone to cavities. Those with a diet high in carbohydrates and sugary foods and residing in communities without fluoridated water are more likely to have cavities. Children and senior citizens are the two groups at highest risk of cavities.
Root cavities, unique to adults occurs from receding gums, leaving parts of your tooth root exposed. As there is no enamel covering over the roots, these exposed areas easily decay. Most people above the age of 60 years have root cavities as a result of gum disease.
Repeated decay around existing fillings – Decay can form around existing fillings and crowns. This is because these areas are not as smooth as a natural tooth surface and can decay easier.
Cavities from dry mouth occurs due to a decrease in saliva.
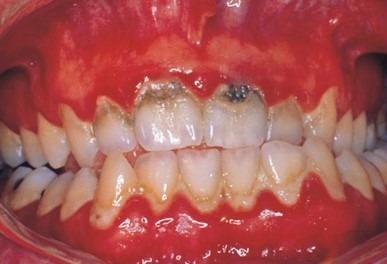


How to protect teeth from caries
The best way to combat cavities is to follow few simple steps:
- Cut down on sweets and in between meals and snacks.
- Brush after every meal and floss daily. Cavities mostly occur in areas which are hard to clean viz. between gaps in teeth and in the pits & fissures and pits.
- Hold the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle and brush inside, outside and between your teeth and on the top of your tongue. Be sure the bristles are firm, not bent, and replace the toothbrush after a few weeks to safeguard against re-infecting your mouth with old bacteria than can collect on the brush.
- Children under six should only use a small pea-sized dab of toothpaste on the brush and should spit out as much as possible because a child’s developing teeth are sensitive to higher fluoride levels.
- Caries is a transmittable disease, toothbrushes should never be shared.
- Visit your dentist once every six months for checkups and professional cleanings.
- If you get a painful toothache, if your teeth are very sensitive to hot or cold foods, or if you notice signs of decay like white spots, tooth discolorations or cavities, make an appointment with your dentist right away. The longer you wait to treat infected teeth the more intensive and lengthier the treatment will be.
- Left neglected, cavities can lead to root canal infection, permanent deterioration of decayed tooth substance and even loss of the tooth itself.
WISDOM TEETH
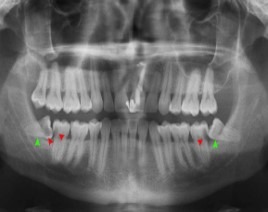
Adults can have a maximum of 32 teeth. The wisdom teeth are the last to come through, right at the back. They usually appear between the ages of 17 and 25. Although sometimes they appear many years later. Nowadays people often have jaws that are too small for all 32 teeth – 28 is often the most we have room for. So, if all the other teeth are present and healthy there may not be enough space for the wisdom teeth to come through properly.
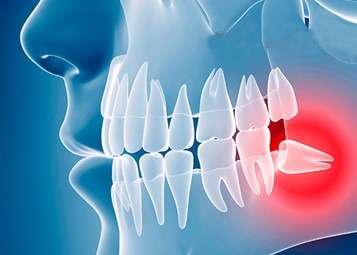
Impacted wisdom tooth
If there is lack of space, the wisdom tooth may try to come through, but gets stuck against the tooth just adjacent to it. Thus, the wisdom tooth will be at an angle, and is described by the dentist as ‘impacted’.
If part of the wisdom tooth has appeared through the gum and part of it is still covered, the gum may become sore and perhaps swollen and painful. Food particles and bacteria can collect under the gum edge, and it will be difficult to clean effectively. Your dentist will advise you whether this is a temporary problem that can be dealt with by using mouthwashes and special cleaning methods (and possibly antibiotics), or to undergo a procedure referred to as operculectomy, that necessarily involves removal of flap of gum covering the tooth or whether it is better to have the tooth removed.
Do’s & Don’ts’ after removal of wisdom tooth
There is usually some swelling and discomfort for a few days afterwards, and it is important to follow any advice you will be given. Usual pain-killers such as paracetamol, asprin or ibuprofen will usually deal with any pain. It is best to stay fairly quiet and relaxed for 24 hours after the procedure to make sure there are no problems in wound healing. There may be some stitches to help the gum heal over. Dentist will probably want to see you again about a week later to check on the healing, and to remove any stitches.
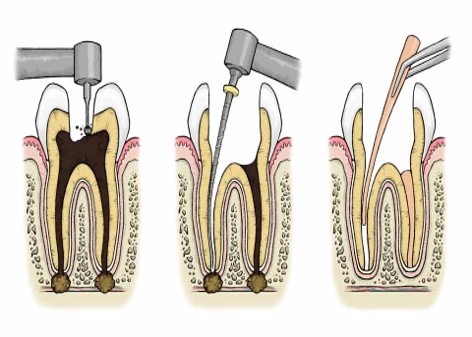
ROOT CANAL TREATMENT
Root Canal Treatment is used to save the tooth which would have otherwise required to be removed. This treatment becomes necessary when the blood or nerve supply of the tooth is infected through decay or injury.
How is the treatment done?
The aim of the treatment is to remove all infection from the root canal. The root is then cleaned and filled to prevent any further infection. Root Canal treatment is a precise and skilled procedure and requires expertise of a specialist. Most courses of treatment involve two or more visits to your dentist. At the first appointment, the infected pulp is removed. Any abscesses, which may be present, can also be drained at this time. The root canal is then cleaned and shaped ready for the filling. A temporary filling is inserted. The tooth is checked at a later visit and when all the infection has cleared, the tooth is permanently filled.
After treatment
It is advisable to restore the tooth with a crown to provide extra support and strength to the root canal treated tooth. Root treated teeth should be treated just the same as any other tooth. Remember to clean your teeth at least once a day, preferably with a fluoride toothpaste. Keep sugary snacks to a minimum, and only to mealtimes if possible. Attend your dentist for regular check-ups.


GUM DISEASE
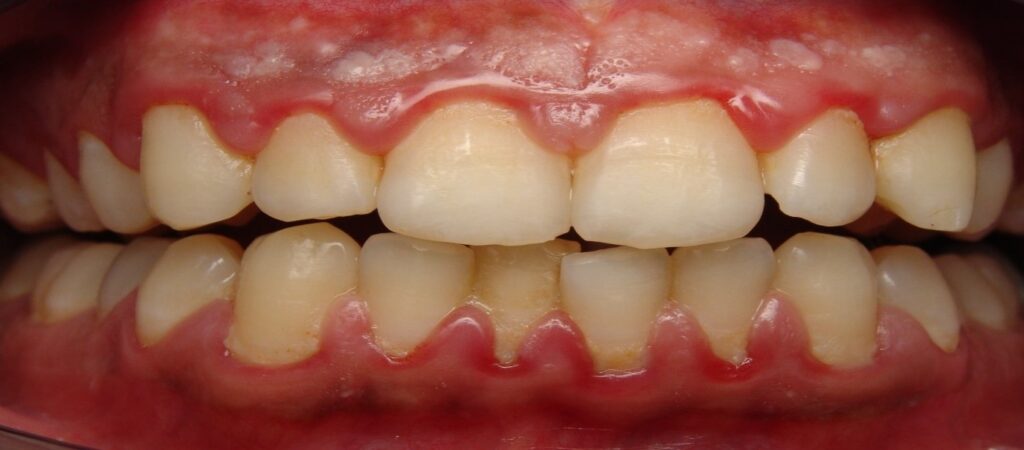
Gum disease describes inflammation or infection of the tissues supporting the teeth. There are two main forms of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontal disease.
Gingivitis refers to inflammation of the gums. Gums around the teeth become very red and swollen, indicating inflammation. Often this swollen gum bleeds when it is brushed during cleaning.
Long-standing gingivitis can progress to periodontal disease. There are a number of forms of periodontal disease and they all affect the supporting structures of the teeth. As the disease progresses the bone anchoring the teeth in the jaw is lost, making the teeth loose. If this is not treated, the teeth may eventually fall out.
Maintenance and treatment
The first thing to do is visit your dentist for a thorough check-up of your teeth and gums.
The best way to treat gum dieses to practice good oral hygiene, although additional dental treatments are required.
For maintaining a good oral hygiene. One should floss regularly to keep the gums clean. Many times, caries affect the gum causing the root to weaken. Have a consultation with your dentist to go for scaling and polishing to clean up your gums.
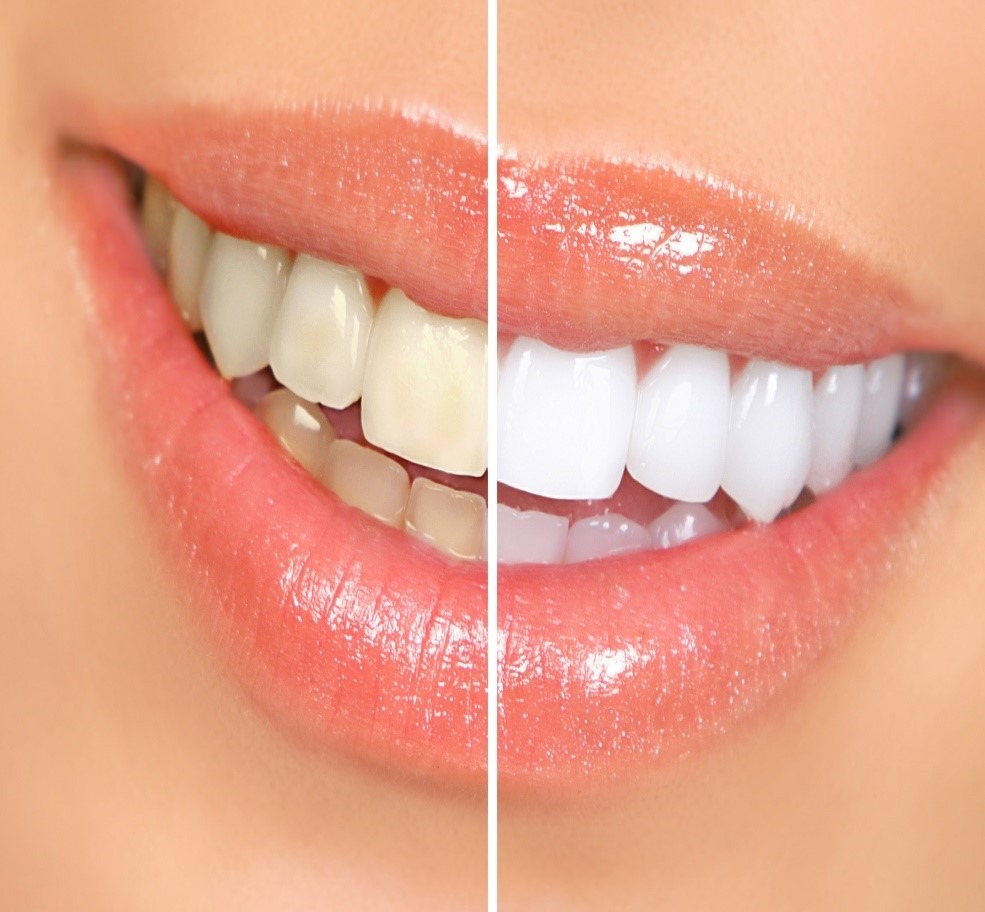
TOOTH WHITENING
Whitening is a bleaching process that lightens discoloration of enamel and dentin. The complete procedure takes less than an hour. The procedure begins with a preparation period followed as little as by 45 minutes of bleaching. (A cleaning is recommended prior to the actual whitening session.)
How long do the results last?
By following some simple post whitening care instructions, your teeth will always be lighter than they were before. To keep your teeth looking their best, we recommend flossing, brushing twice daily, and occasional touch-ups with bleaching. These are professional formula products designed specifically to keep your teeth their brightest. They are available only through your dental professional.
Are there any side effects?
Sensitivity during the treatment may occur with some patients. The light generates minimal heat which is the usual source of discomfort. On rare occasions, minor tingling sensations are experienced immediately after the procedure, but always dissipate. You can also ask your dentist to supply you with anti-sensitivity toothpaste for use prior to treatment.
Is whitening safe?
Yes. Extensive research and clinical studies indicate that whitening teeth under the supervision of a dentist is safe. In fact, many dentists consider whitening the safest cosmetic dental procedure available. As with any tooth whitening product, Teeth Whitening is not recommended for children under 13 years of age and pregnant or lactating women.






PREGNANCY & DENTAL HEALTH
Does pregnancy affect oral health
Expecting mothers (and women taking oral contraceptives) experience elevated levels of hormones estrogen and progesterone. This causes the gums to react differently to the bacteria found in plaque, and results in a condition known as “pregnancy gingivitis.” Symptoms include swollen, redness and bleeding of the gums when you brush. Remember that the bacteria in plaque (not hormones) is what causes gingivitis. Brush twice a day and floss before you go to bed to help avoid plaque buildup.
Can gum disease affect baby’s health?
New research suggests a link between pre-term, low birth weight babies and gingivitis. Excessive bacteria, causing gingivitis, can enter the bloodstream through your mouth (gums). If this happens, the bacteria can travel to the uterus, triggering the production of chemicals called “prostaglandins,” which are suspected to induce premature labor.
Is treatment required during pregnancy?
Good oral health care is vital during your pregnancy. Continue with your regular dental cleaning and check-ups to avoid oral infections that can affect the fetus, such as gingivitis and periodontal disease. Dentists recommend that major dental treatments that aren’t urgent be postponed until after your child is born. The first trimester, the stage of pregnancy in which most of the baby’s organs are formed, is the most crucial to your baby’s development, so it is best to have procedures performed during the second trimester to minimize any potential risk. Dental work is not recommended during the third trimester.
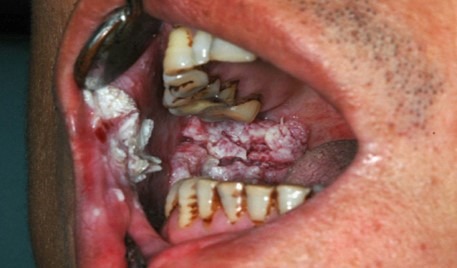
FACTS AND MYTHS ON ORAL CANCER
Betel nuts tobacco chewers are more prone to oral cancer, although genetics, diet, environment and immune system also play a part.
Several white and red lesions of the mouth caused by betel nut and tobacco chewing shall definitely improve if lesions are identified and habit is stopped in time.
Pain is usually a late sign of oral cancer, but pain in the head and neck region should not be ignored.
There are side effects to all form of Oral Cancer treatment.